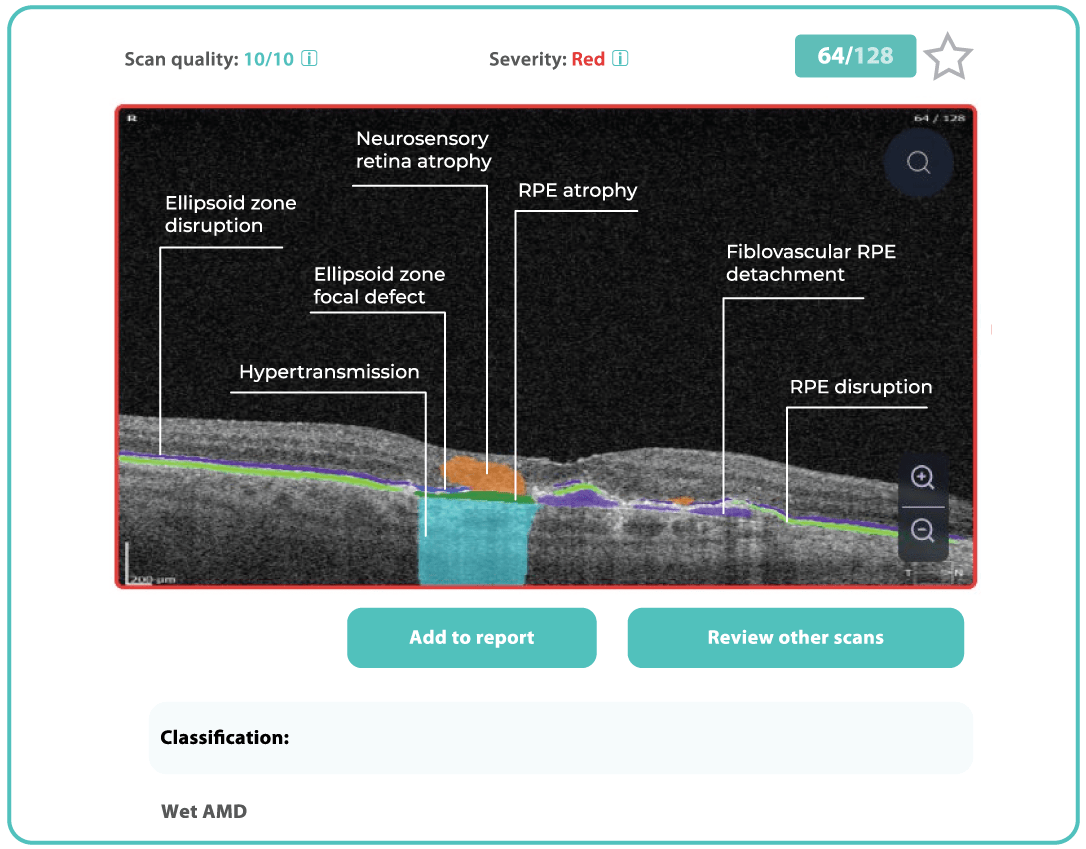
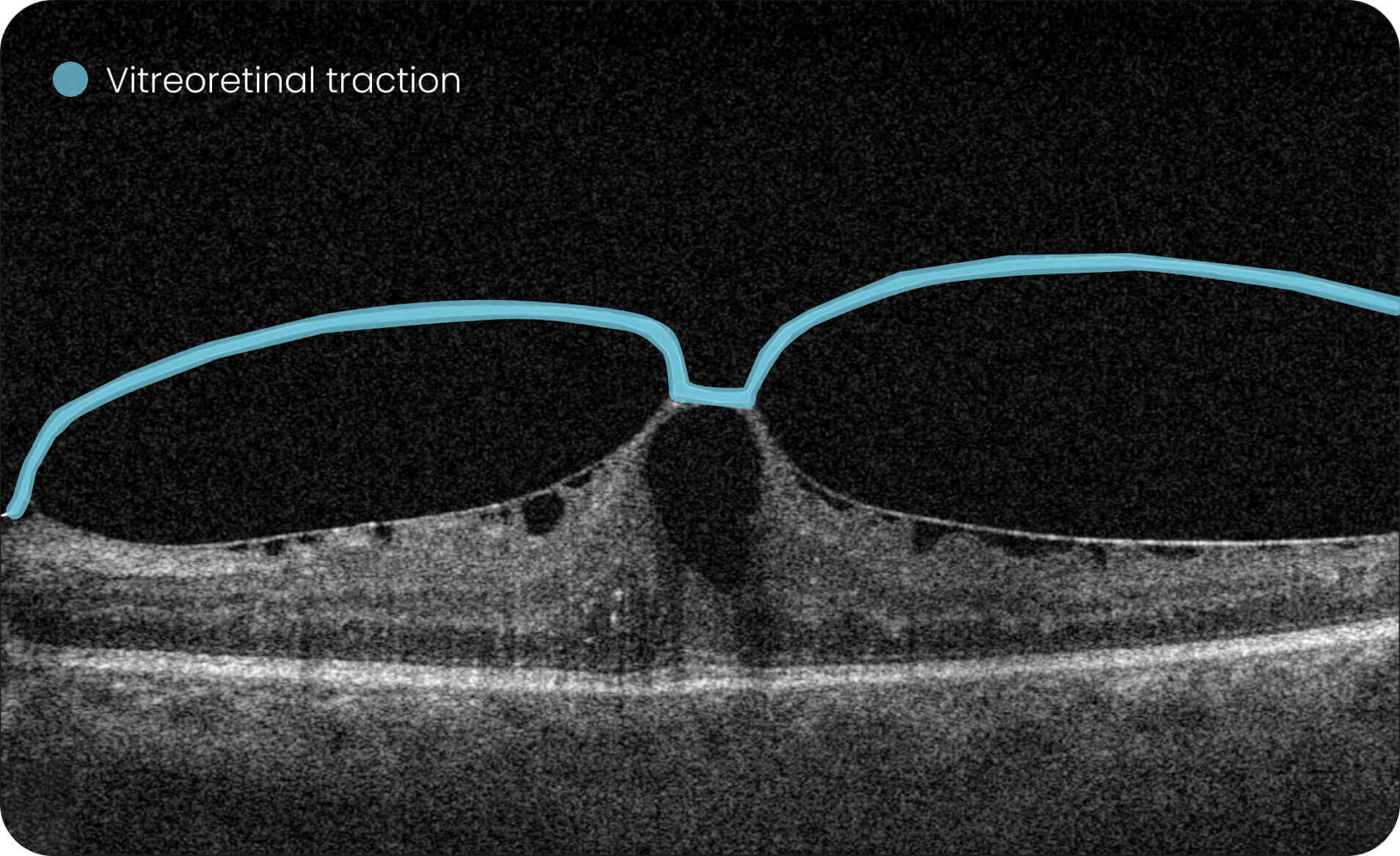
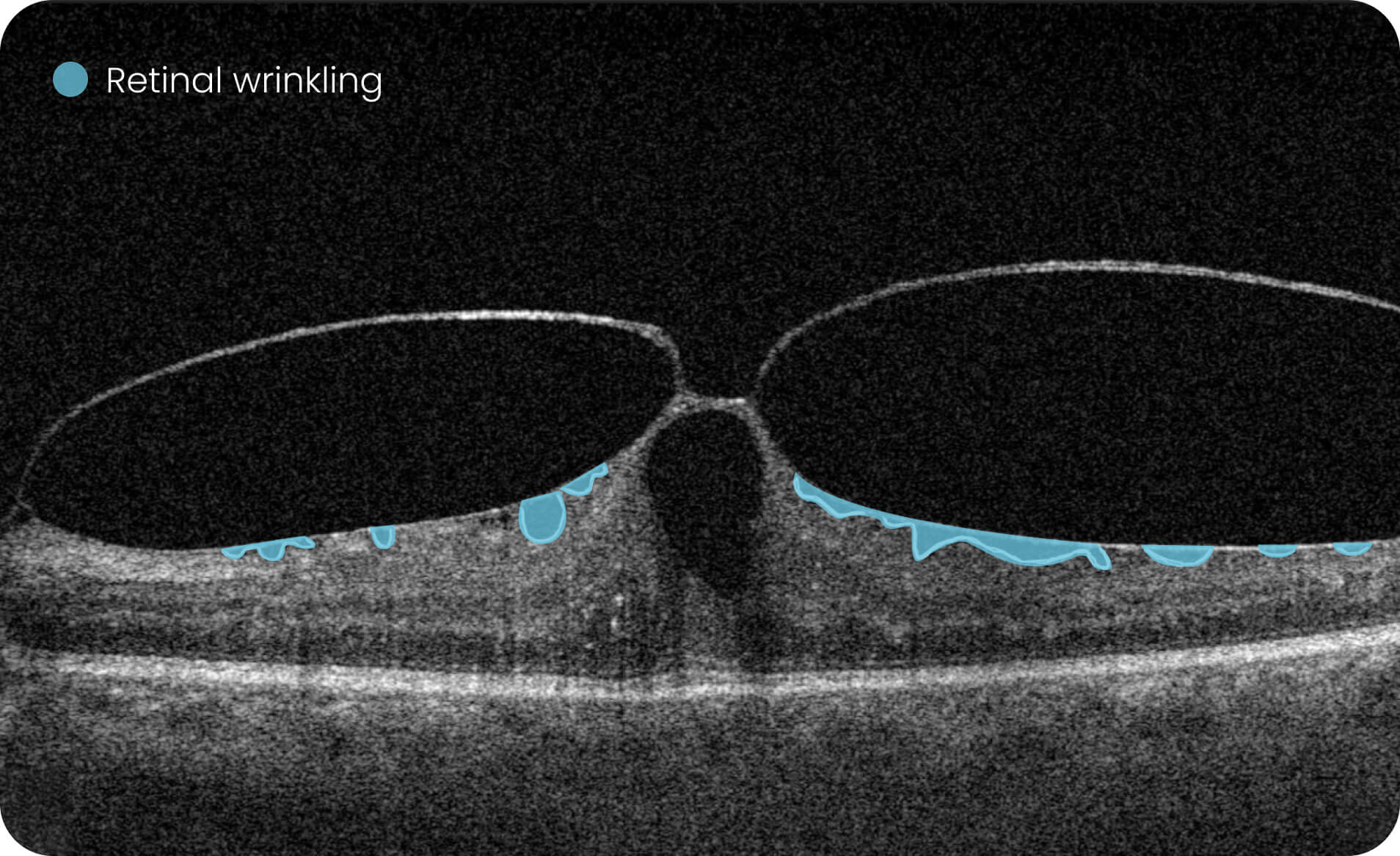
AI-powered OCT analysis is the most effective and reliable diagnostic method today. OCT AI is used by 300+ businesses all over the world.
- Altris AI differentiates between pathological and non-pathological b-scans
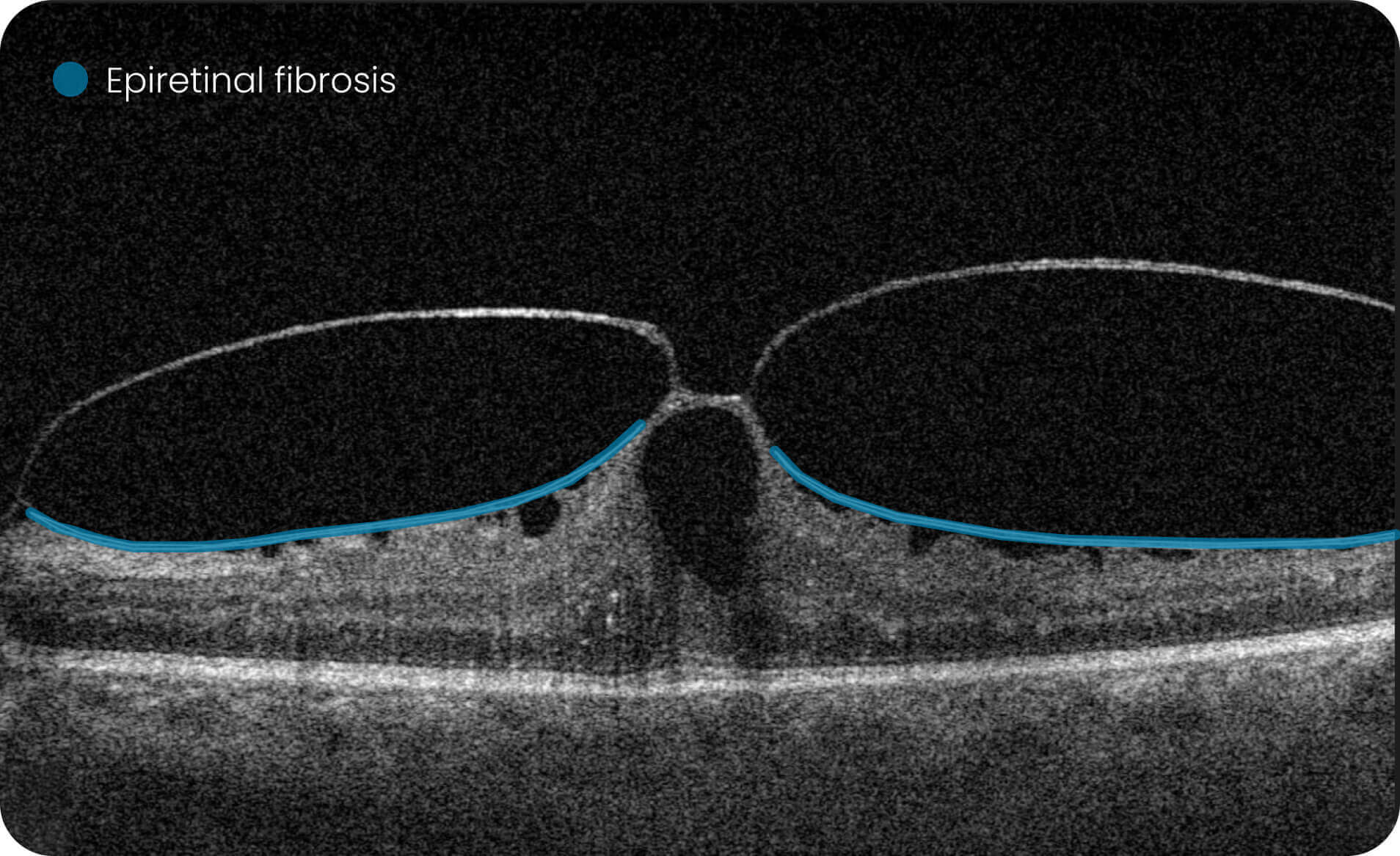
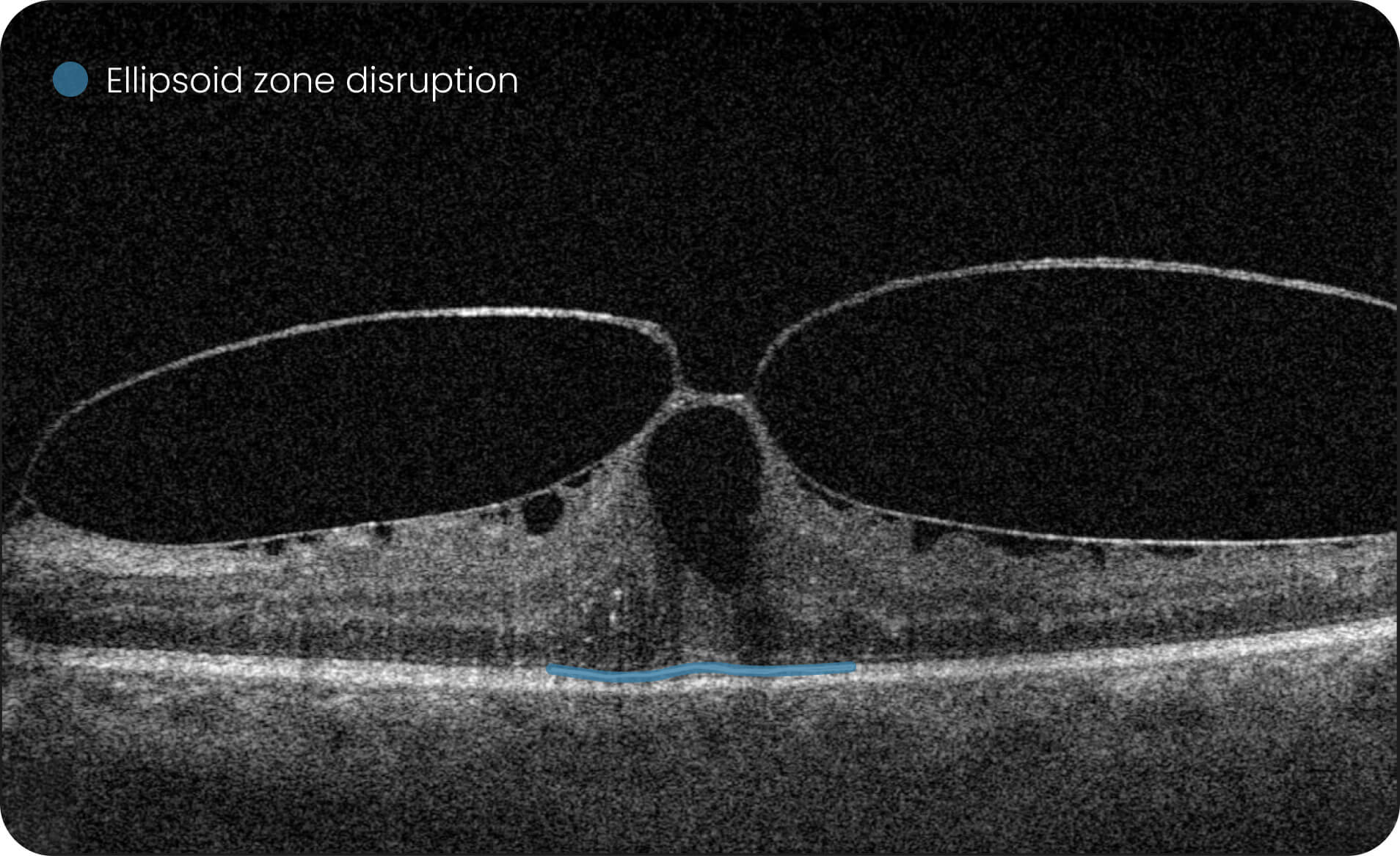
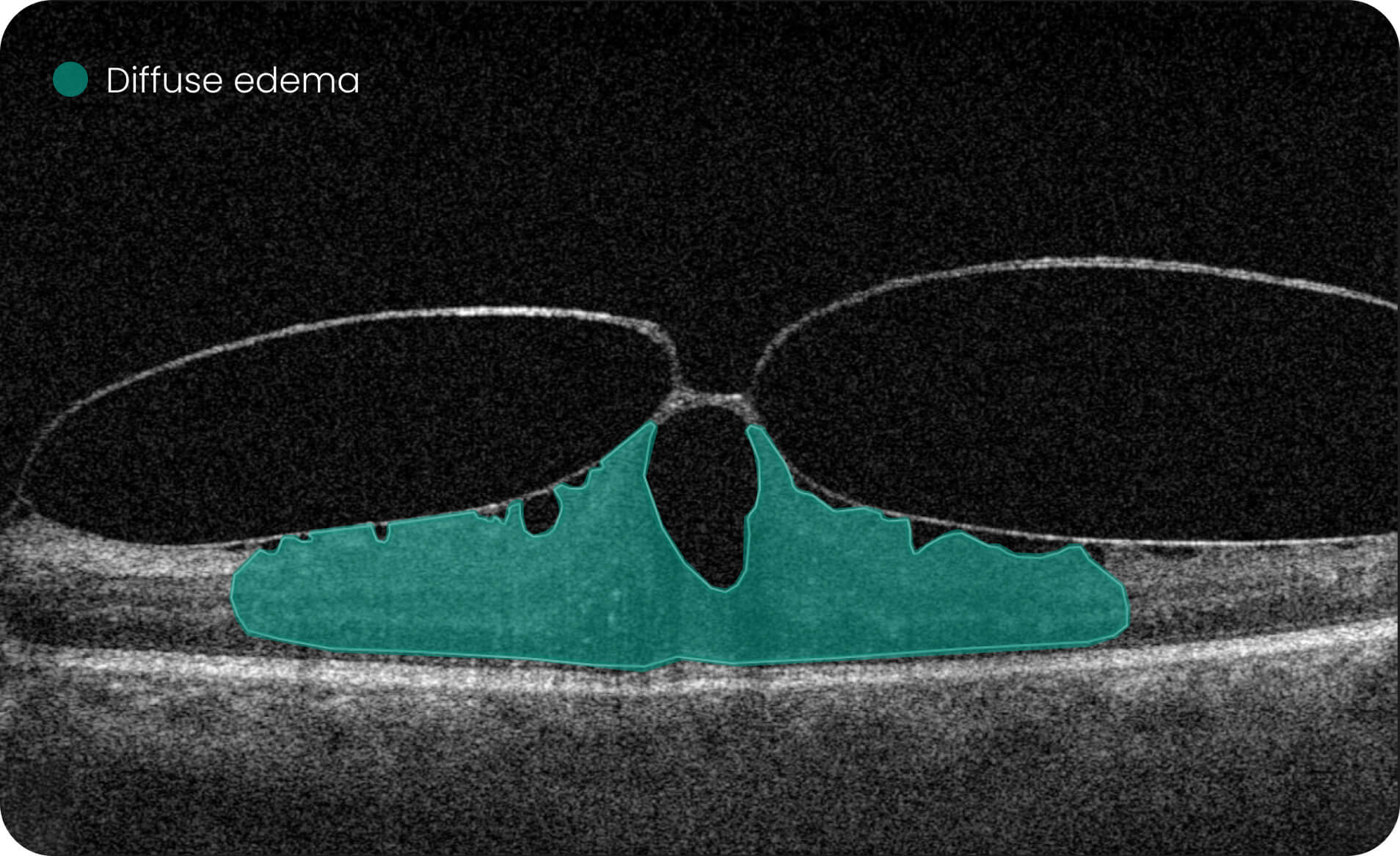
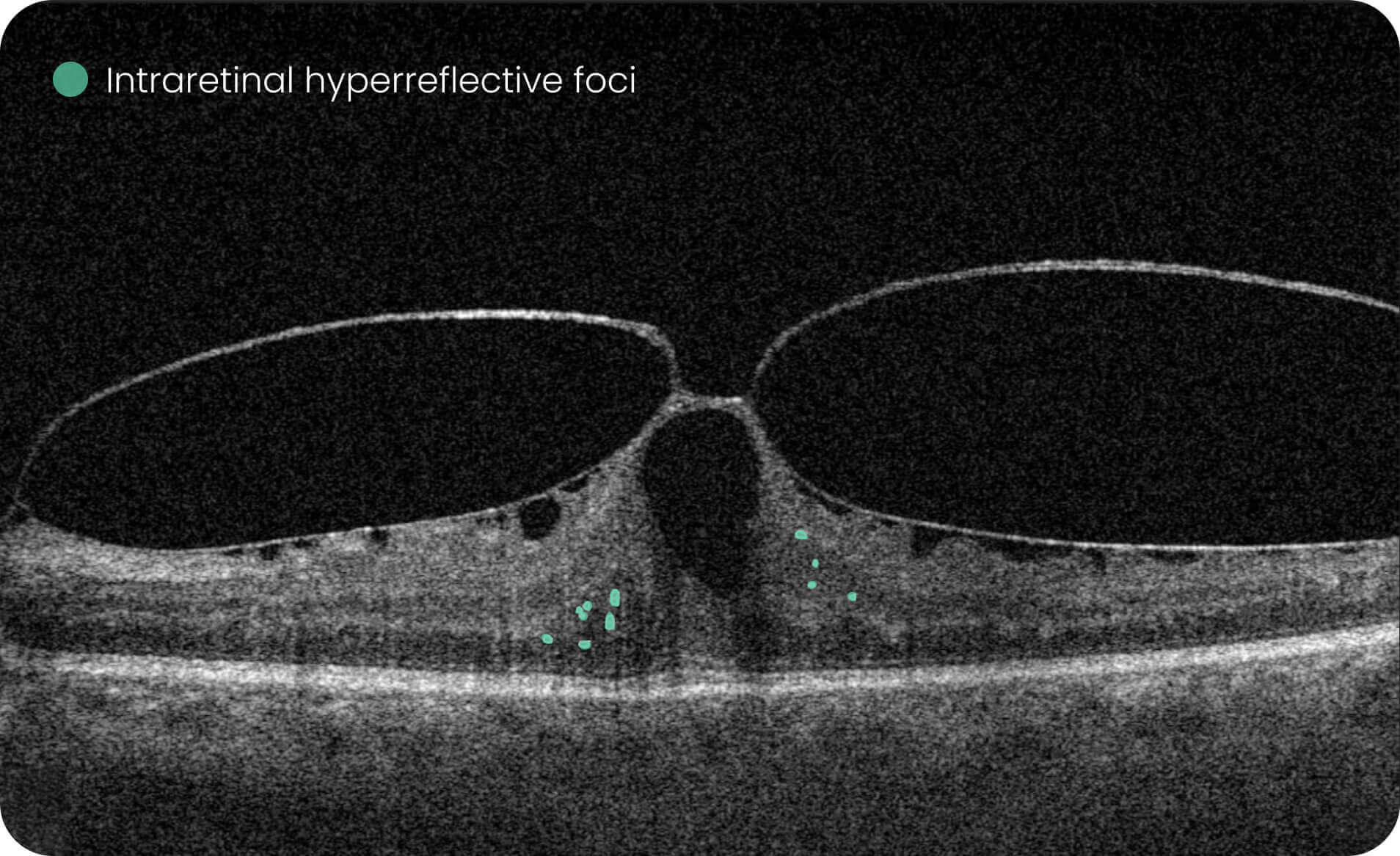
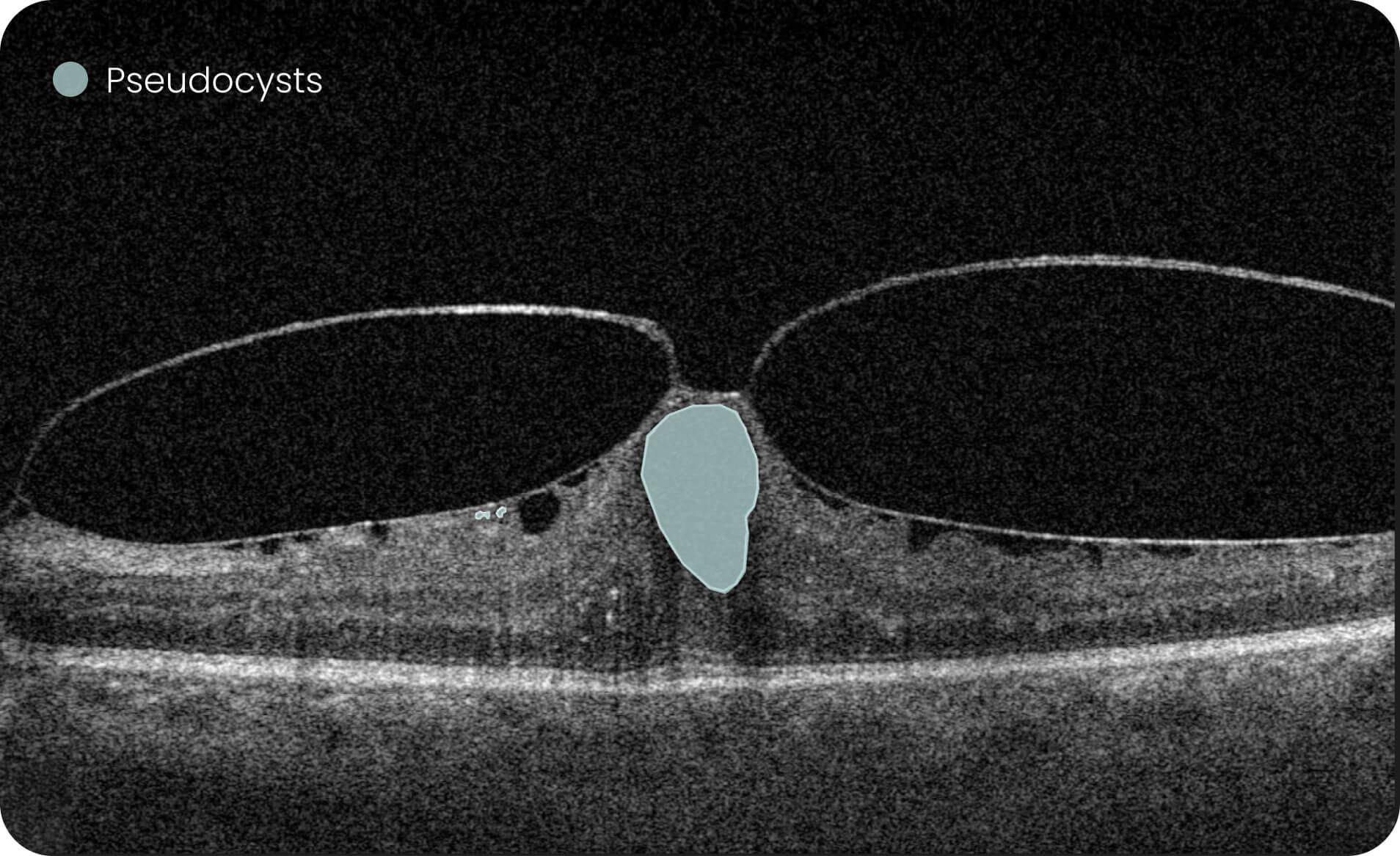
- Altris AI detects 70+ retina pathologies and biomarkers
- Altris AI assesses the risk of early glaucoma
If you want to learn more, take a look at the brochure.






Platform overview
Only practical features for ophthalmologists and other doctors
The security of patients’ data is our top priority: we are GDPR compliant, all data is encrypted, CE-certified, and FDA- cleared (510k).
The AI-powered ophthalmic image management system is an effective solution for any clinic that uses OCT equipment for diagnostics.
It is implemented in 30+ modern eye clinics around the world and is used by thousands of eye care professionals all over the world.
Empowerment of each eye care specialist with modern Artificial Intelligence tool that gives confidence
More effective triage of patients
Routine workflow optimisation
Making eye care business truly high-techand profitable
What's the value of Altris AI?
And how it works
Altris AI is a web platform created by retina experts for all eye care specialists in the world.
We’ve collected millions of OCT scans, and our team graphically labeled thousands of them to
create the Altris AI system that can:
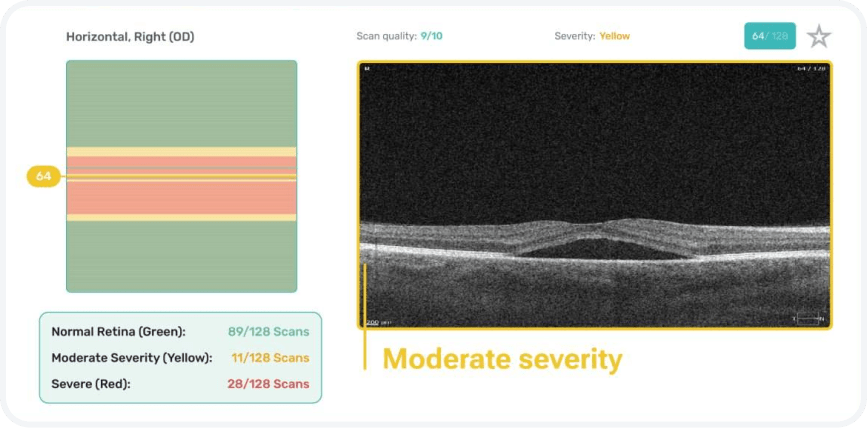
Differentiate between high, medium, and low-severity scans within a minute
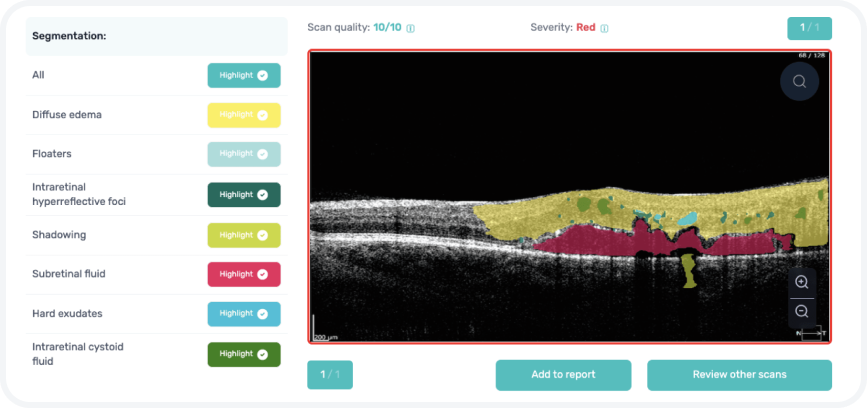
Detect 70+ pathologies and pathological signs, including some most widespread
pathologies, such as Diabetic Retinopathy, as well as rare pathological signs

Formats
DICOM format will help you to extract maximum information. However, the system works with all data formats, such as jpg, and png

OCT equipment
Altris AI is vendor-neutral. We work with all the OCT equipment producers

OCT reports
We create comprehensible OCT reports for patients and doctors
Services
What you get with Altris AI:
Contact us- Personal Manager Support
- Severity differentiation
- Layers
- EDTRS
- Pathologies Segmentation + Classification
- Progression Tracking EDTRS
- Reports
- Referral Score
- Glaucoma Risk Analysis
- Manual Measurements
How it goes?
We support you through the whole way
Contact usWhat you get:
- Onboarding training for the whole team
- Unlimited number of OCT examinations: we adjust to your needs
- DICOM files extraction support: we attune the process until it works
- Customization (adding features your team needs). We make the system for your needs
- Personal support throughout the whole process of digitalization
- Cloud/ On-premises data storage for advanced security
- Integration support with any EHR, EMR system
- Marketing support: we provide you with materials to show that your business is AI-powered